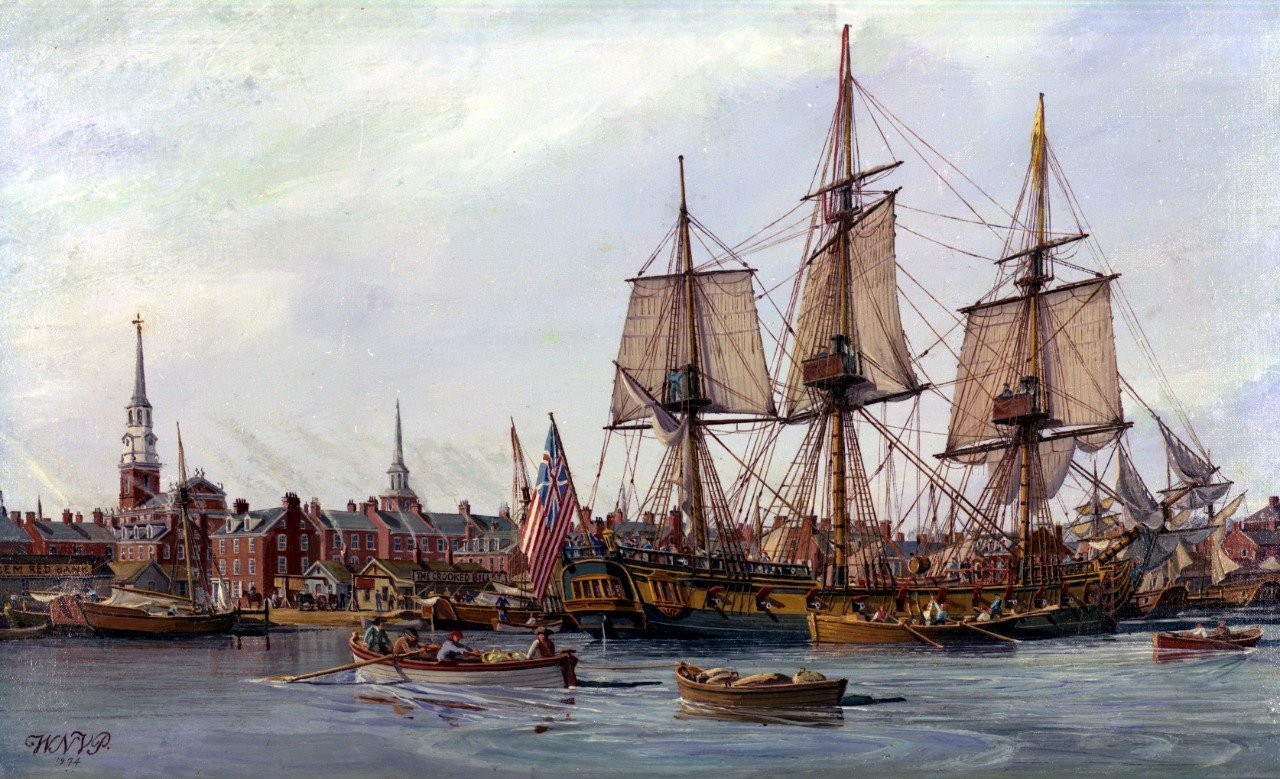A list of specific military models that are ordered chronologically by the year they were launched. Also, a list of certain centuries, wars, and historic events are coherently listed alongside the models for reference as seen below. Some models were built before a historic event(s) and will state which period(s), war(s), and/or battle(s) they belong in.
Timeline of museum’s military models

16th–19th
century
January 1, 1501 – December 31, 1800
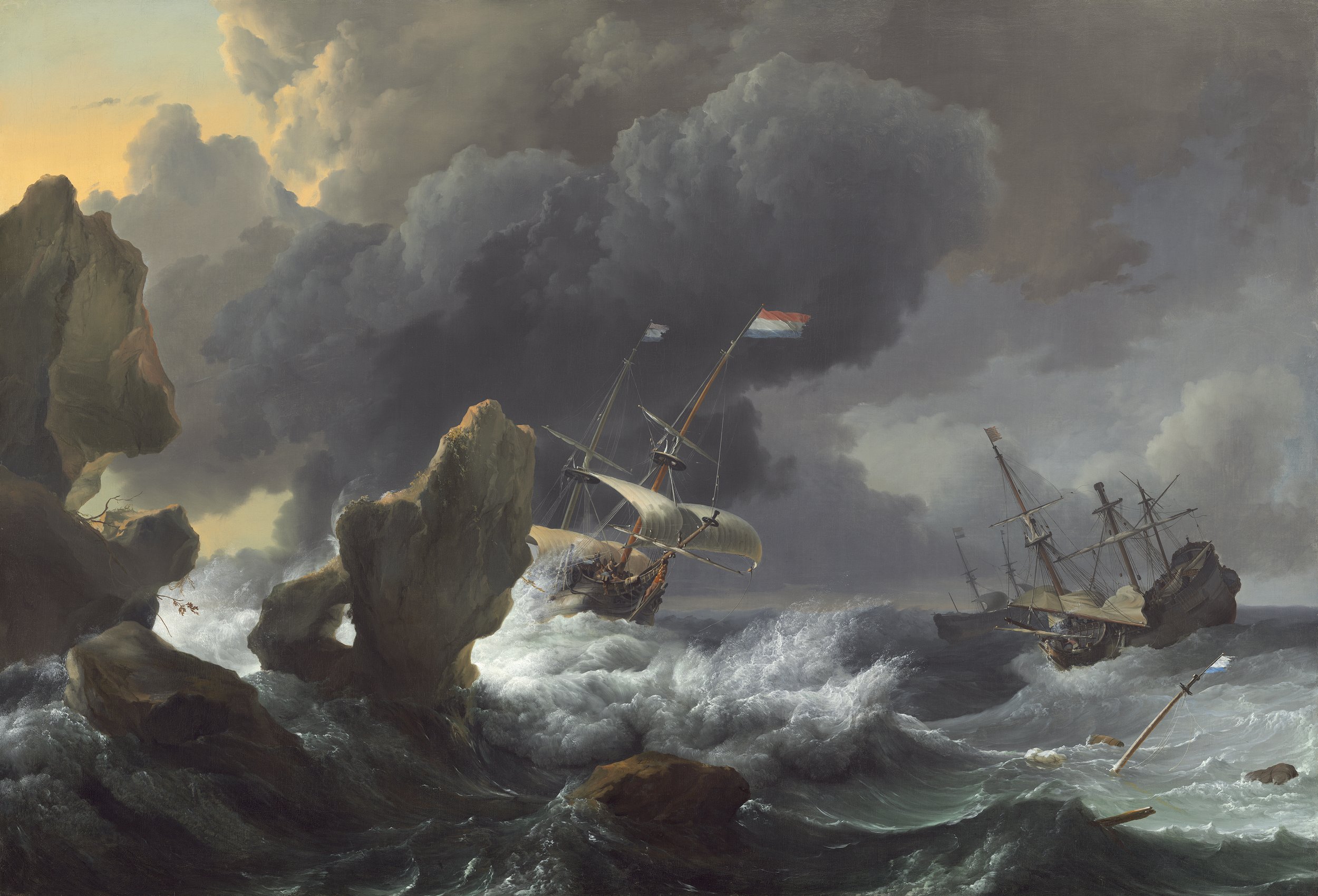
Image: Ludolf Backhuysen, Ships in Distress off a Rocky Coast, 1667, oil on canvas, National Gallery of Art, Washington.16th – 19th Century
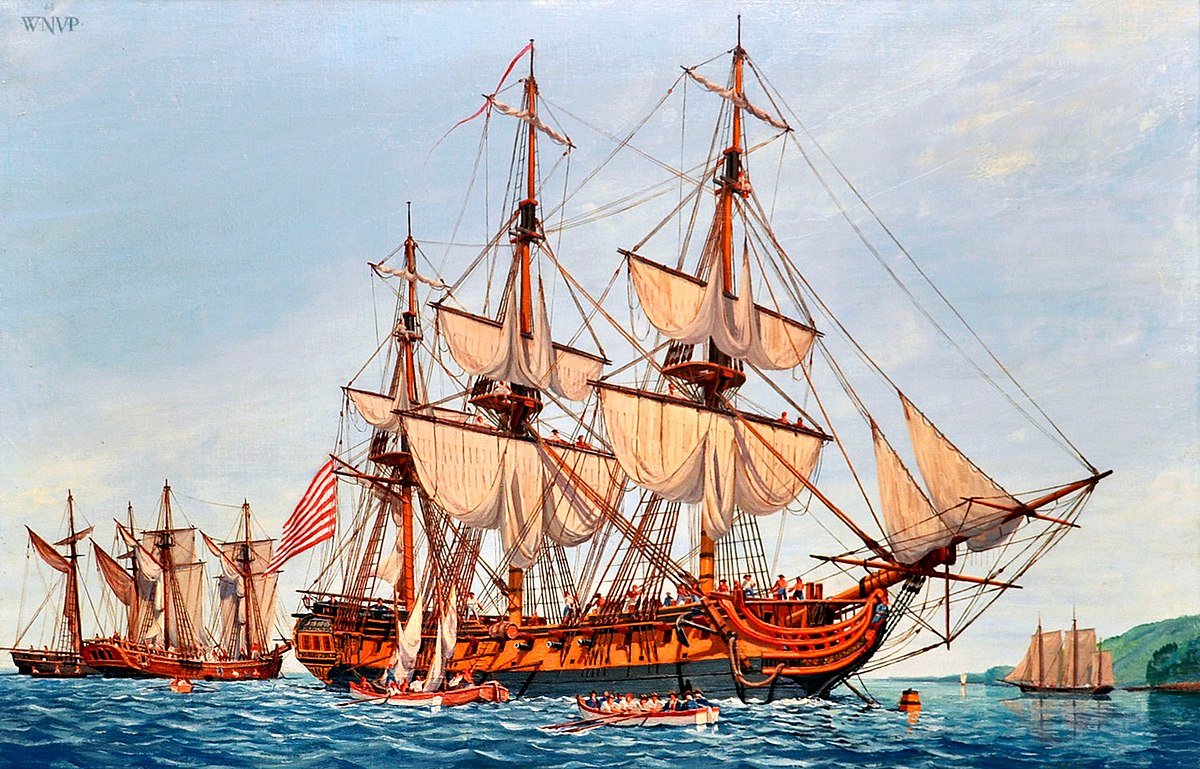
Xebec Frigate
Scale 1/48
A xebec (/ˈziːbɛk/ or /zɪˈbɛk/), also spelled zebec, was a Mediterranean sailing ship that was used mostly for trading. Xebecs had a long overhanging bowsprit and aft-set mizzen mast. The term can also refer to a small, fast vessel of the sixteenth to nineteenth centuries, used almost exclusively in the Mediterranean Sea.
1766 – September 4, 1779
USS Bohomme Richard
Scale 1/50
Bonhomme Richard, formerly Duc de Duras, was a warship in the American Continental Navy named for Founding Father Benjamin Franklin. She was originally an East Indiaman, a merchant ship built in France for the French East India Company in 1765, for service between France and Asia. She was placed at the disposal of John Paul Jones on 4 February 1779, by King Louis XVI of France as a result of a loan to the United States by French shipping magnate Jacques-Donatien Le Ray.
part of:
American Revolutionary War
Battle of Flamborough Head
1774– 1782
USS Alfred
Scale 1/48
Alfred was the merchant vessel Black Prince, named for Edward, the Black Prince, and launched in 1774. The Continental Navy of what would become the United States Navy acquired her in 1775, renamed her Alfred after 9th-century English monarch Alfred the Great and commissioned her as a warship. She participated in two major actions, the battle of Nassau, and the action of 6 April 1776. The Royal Navy captured her in 1778, took her into service as HMS Alfred, and sold her in 1782. She then became the merchantman Alfred and sailed between London and Jamaica.
Part of:
American Revolutionary War
Raid of Nassau
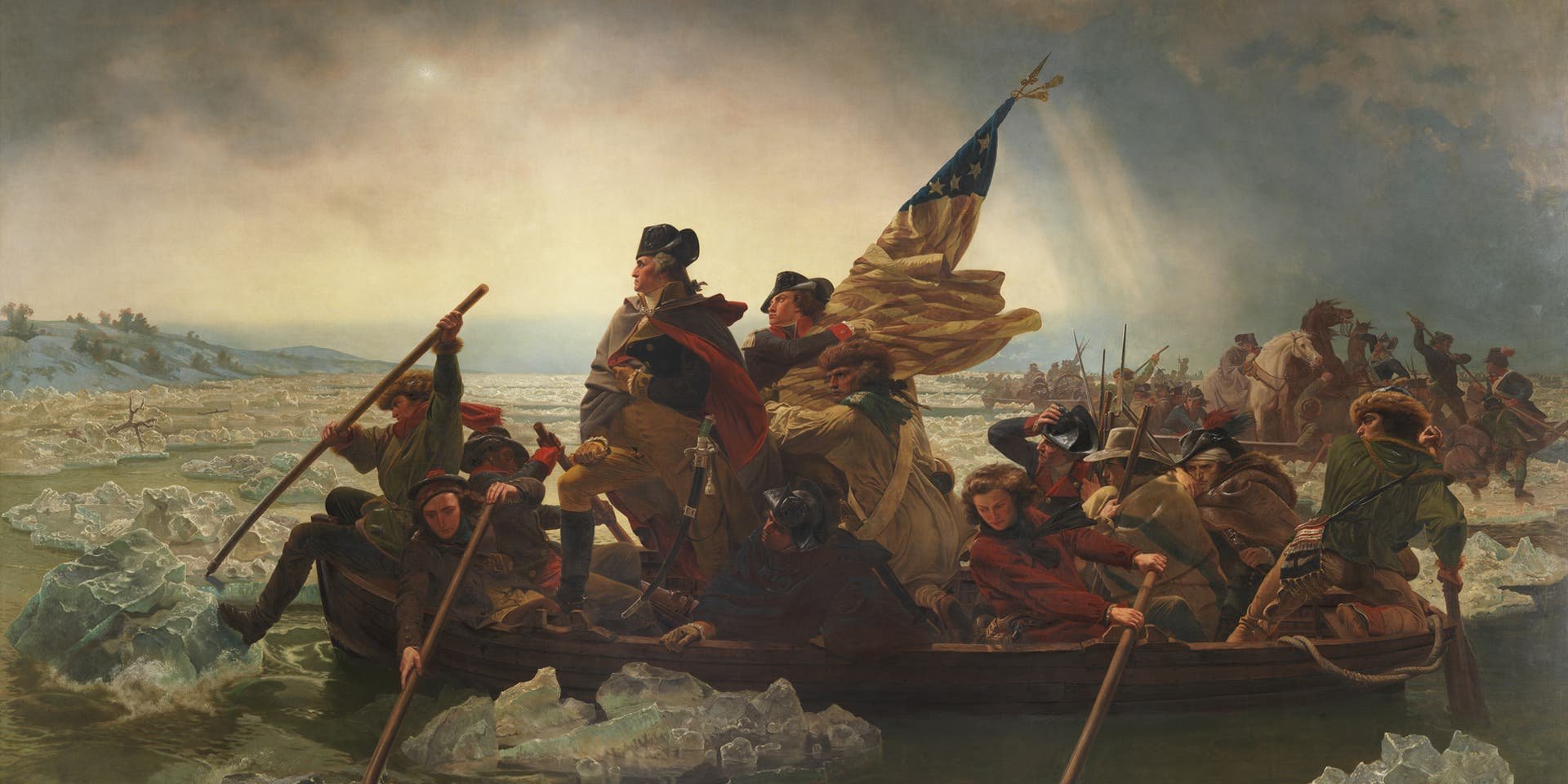

American
Revolutionary war
April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783
image: THE METROPOLITAN MUSEUM OF ARTJuly 4, 1776
United States signed the declaration of independence
November 8, 1778 – March 1782
USS Confederacy
Scale 1/48
USS Confederacy was a 36-gun sailing frigate of the Continental Navy in the American Revolutionary War. The British Royal Navy captured her in March 1781. The British named her Confederate but never commissioned her. She reached England in about half-a-year and was broken up in 1782.
Part of:
American Revolutionary War
May 5, 1789 – November 9, 1799
French Revolution
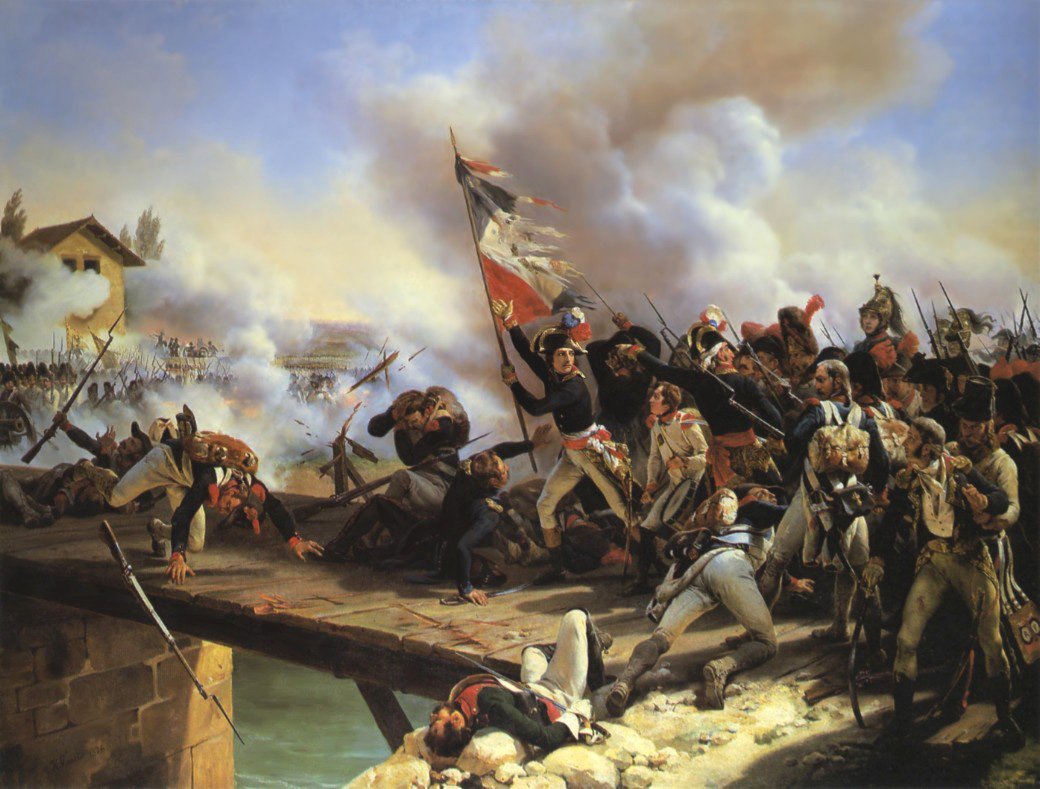

French
Revolutionary Wars
April 20, 1792 – March 27, 1802
Image: Liberty Leading the People by Eugène Delacroix, 1830. Medium Oil on canvas. Dimensions 260 cm × 325 cm (102.4 in × 128.0 in). Louvre, Paris.April 24, 1790 – June 28, 1814
HMS Leopard
Scale 1/50
HMS Leopard was a 50-gun Portland-class fourth rate of the Royal Navy. She served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and was notable for the actions of her captain in 1807, which were emblematic of the tensions that later erupted in the War of 1812 between Britain and America. She was wrecked in 1814.
Part of:
French Revolutionary Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Chesapeake-Leopard Affair
May 10, 1797 – April 20, 1861
USS UNITED STATES
Scale 1/58
USS United States was a wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy and the first of the six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794. The name "United States" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so the United States and her sisters were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Humphrey's shipyard in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and launched on 10 May 1797 and immediately began duties with the newly formed United States Navy protecting American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France.
Part of:
Quasi–War
War of 1812
United States vs Macedonian
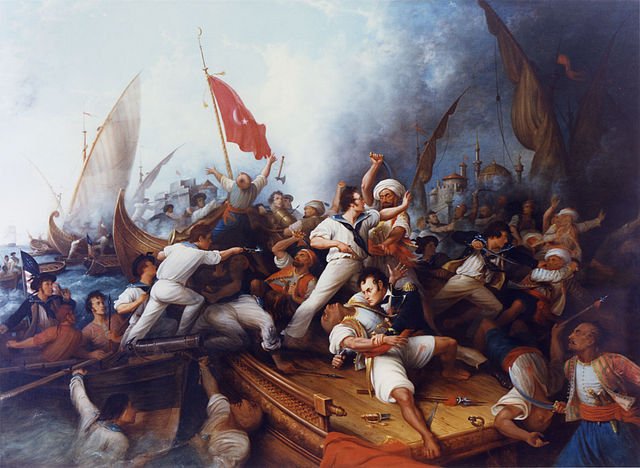
Second Barbary War
October 21, 1797 – Present Day
USS Constitution
Scale 1/72
USS Constitution, also known as Old Ironsides, is a three-masted wooden-hulled heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She is the world's oldest ship still afloat. She was launched in 1797, one of six original frigates authorized for construction by the Naval Act of 1794 and the third constructed. The name "Constitution" was among ten names submitted to President George Washington by Secretary of War Timothy Pickering in March of 1795 for the frigates that were to be constructed. Joshua Humphreys designed the frigates to be the young Navy's capital ships, and so Constitution and her sister ships were larger and more heavily armed and built than standard frigates of the period. She was built at Edmund Hartt's shipyard in the North End of Boston, Massachusetts. Her first duties were to provide protection for American merchant shipping during the Quasi-War with France and to defeat the Barbary pirates in the First Barbary War.
Part of:
Quasi–War
First Barbary War
Battle of Tripoli Harbor
War of 1812
Consitution vs. Guerriere
Constitution vs. Java
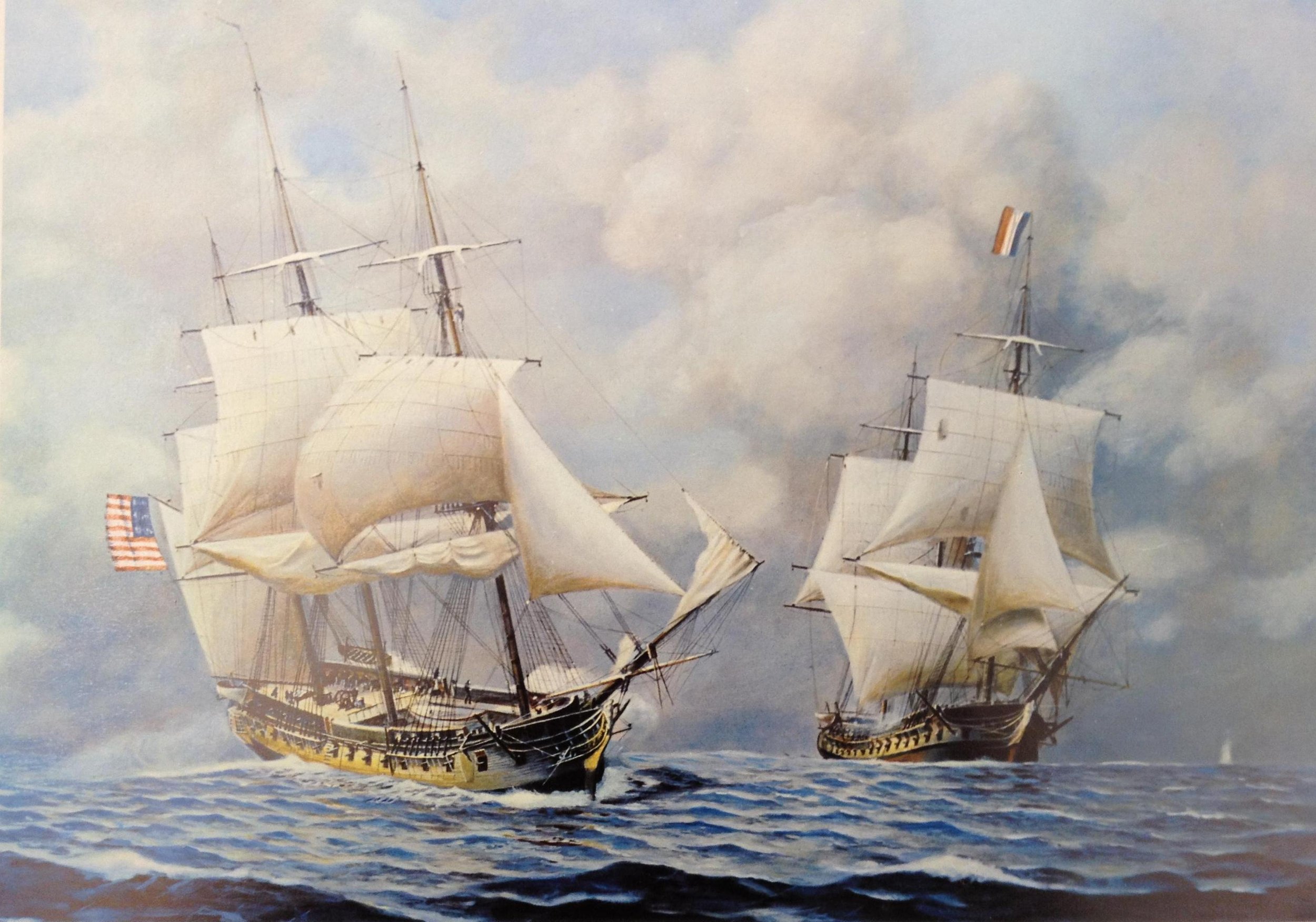

Quasi-War
July 7, 1798 – September 30, 1800
Image: Quasi-War, 1798-1801, USS Constellation vs. l’Insurgente – 9, February 1799, Reproduction of oil painting by John W. Schmidt, Print Collection, MdHS.September 30, 1799 – June 6, 1837
USS Essex
Scale 1/58
The first USS Essex of the United States Navy was a 36-gun or 32-gun sailing frigate that participated in the Quasi-War with France, the First Barbary War, and in the War of 1812. The British captured her in 1814 and she then served as HMS Essex until sold at public auction on 6 June 1837.
Part of:
First Barbary War
War of 1812
May 10, 1801 – June 10, 1805
First Barbary War
May 18, 1803 – November 20, 1815
Napoleonic Wars
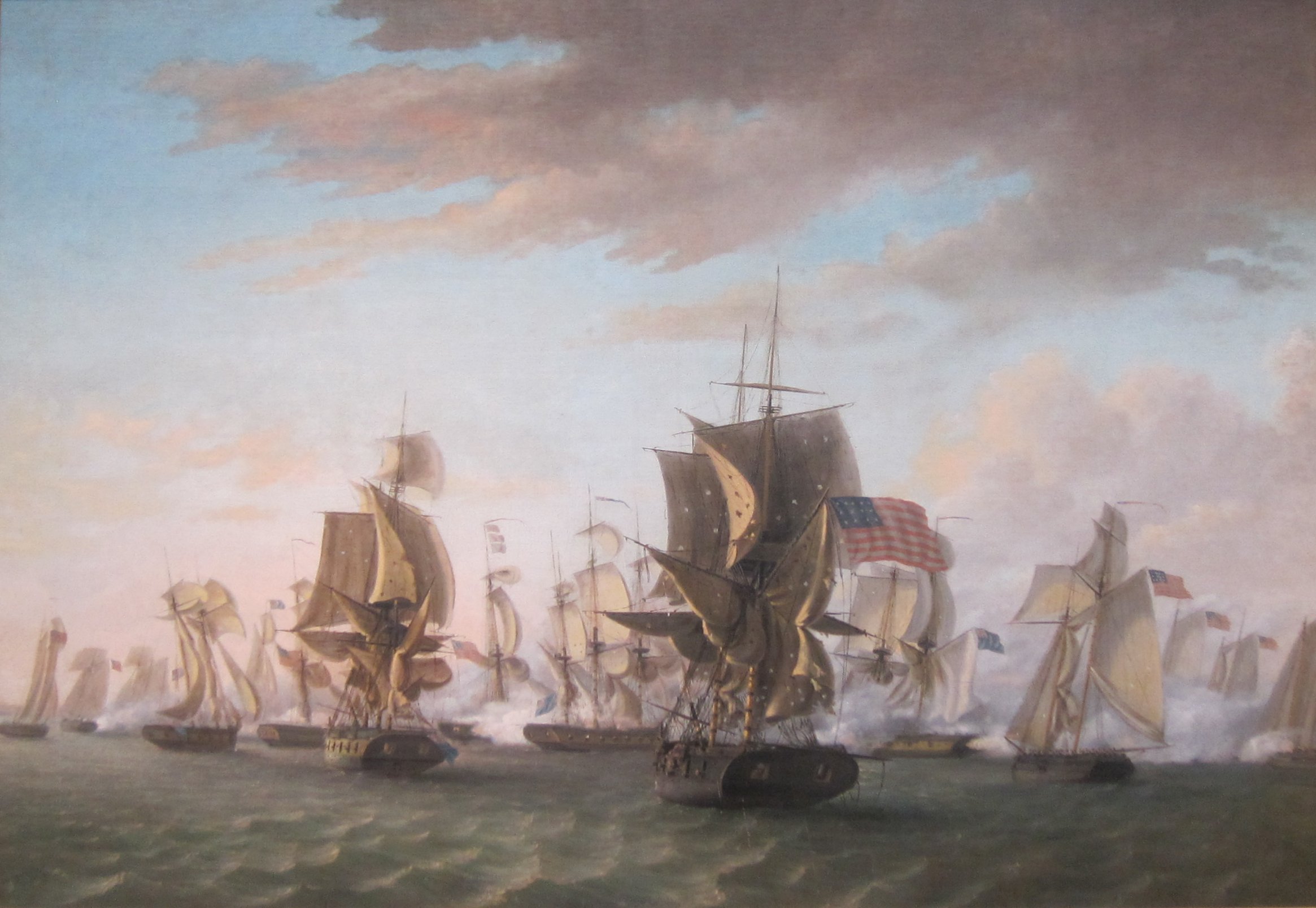

War of 1812
June 18, 1812 – February 17, 1815
Image: Perry's Victory on Lake Erie by Thomas Birch, Oil on canvas, c. 1814. Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts, Philadelphia; Gift of Mrs. Charles H.A. Esling.1812 – June 22 (or July 11), 1814
USS Rattlesnake
Scale 1/48
USS Rattlesnake was the brig Rambler built in Medford, Massachusetts, in 1812 that the United States Navy purchased in July 1813. Rattlesnake captured numerous British merchant vessels before HMS Leander captured her in mid-1814. The Royal Navy apparently purchased her in Nova Scotia, but there is no record of her subsequent career.
Part of:
War of 1812
June 17 - 19, 1815
Second Barbary War
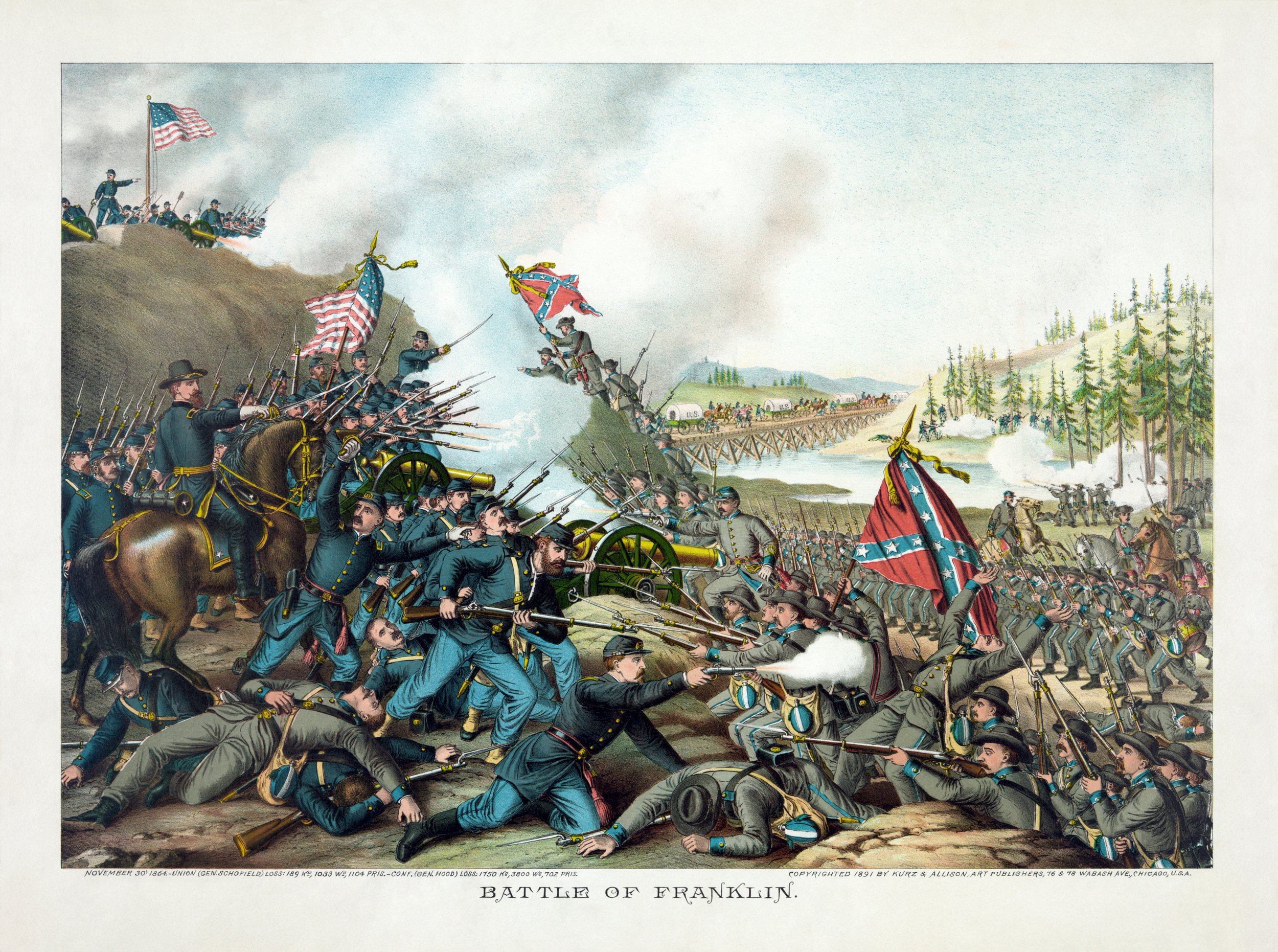

April 12, 1861 – April 9, 1865
Civil war
Image: Battle of Franklin. November 30, 1864. United States Library of Congress's Prints and Photographs division
under the digital ID pga.01852January 30, 1862 – December 31, 1862
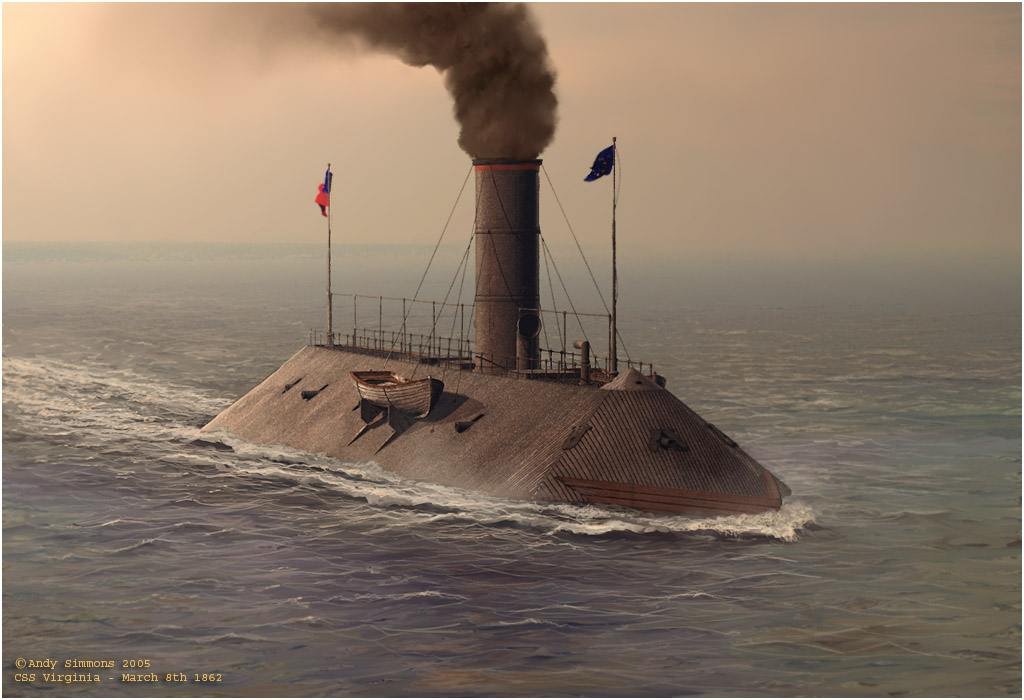
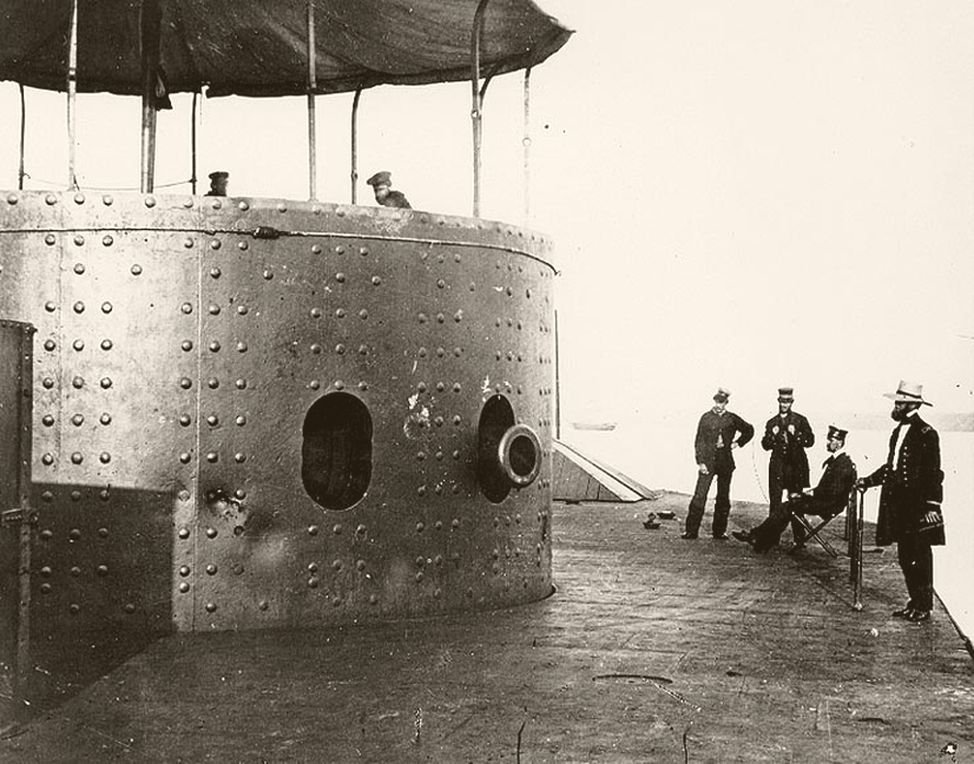
USS Monitor
Scale 1/120
USS Monitor was an ironclad warship built for the Union Navy during the American Civil War and completed in early 1862, the first such ship commissioned by the Navy. Monitor played a central role in the Battle of Hampton Roads on 9 March under the command of Lieutenant John L. Worden, where she fought the casemate ironclad CSS Virginia (built on the hull of the scuttled steam frigate USS Merrimack) to a stalemate. The design of the ship was distinguished by its revolving turret, which was designed by American inventor Theodore Timby; it was quickly duplicated and established the monitor class and type of armored warship built for the American Navy over the next several decades.
Part of:
Civil War
Battle of Hampton Roads
February 17, 1862 – May 11, 1862
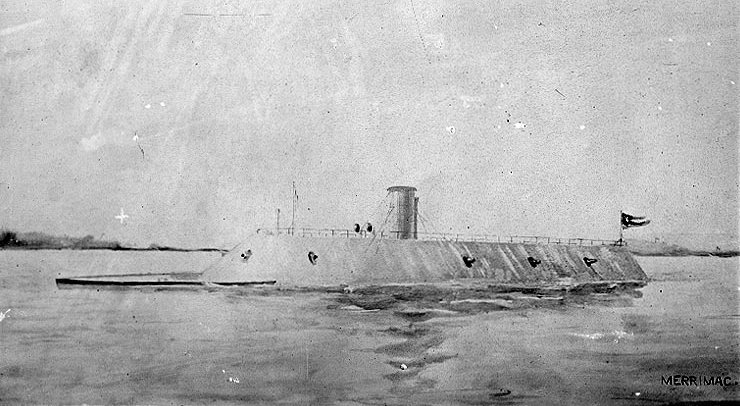
CSS Virginia
Scale 1/120
CSS Virginia was the first steam-powered ironclad warship built by the Confederate States Navy during the first year of the American Civil War; she was constructed as a casemate ironclad using the razéed (cut down) original lower hull and engines of the scuttled steam frigate USS Merrimack. Virginia was one of the participants in the Battle of Hampton Roads, opposing the Union's USS Monitor in March 1862. The battle is chiefly significant in naval history as the first battle between Ironclads.
Part of:
Civil War
Battle of Hampton Roads
July 29, 1862 – June 19, 1864
CSS Alabama
Scale 1/95
CSS Alabama was a screw sloop-of-war built in 1862 for the Confederate States Navy. It was built in Birkenhead on the River Mersey opposite Liverpool, England by John Laird Sons and Company. Alabama served as a successful commerce raider, attacking Union merchant and naval ships over the course of her two-year career. She was sunk in June 1864 by USS Kearsarge at the Battle of Cherbourg outside the port of Cherbourg, France.
Part of:
Civil war
April 21 – August 13, 1898
Spanish–American War
Image: Rough Riders, Colonel Theodore Roosevelt, during the Spanish-American War, 1898. Everett Collection Historical.November 18, 1889 – February 15, 1898
USS Maine (1889)
Scale 1/125
Maine was a United States Navy ship that sank in Havana Harbor on February 15, 1898, contributing to the outbreak of the Spanish–American War in April. U.S. newspapers, engaging in yellow journalism to boost circulation, claimed that the Spanish were responsible for the ship's destruction. The phrase, "Remember the Maine! To hell with Spain!" became a rallying cry for action. Although the Maine explosion was not a direct cause, it served as a catalyst that accelerated the events leading up to the war.
Part of:
What began the Spanish–American War
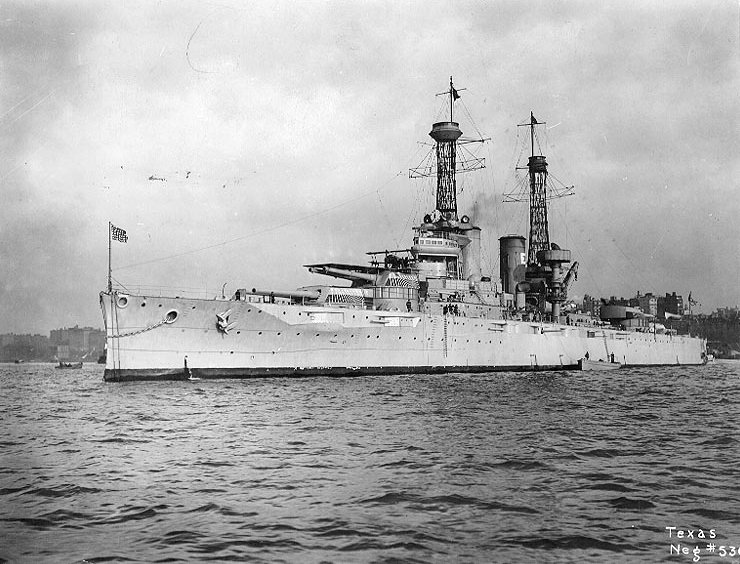
June 28, 1892 – March 21–22, 1911
USS Texas (1892)
Scale 1/192
USS Texas was a pre-dreadnought battleship built by the United States in the early 1890s. The first American battleship commissioned, she was built in reaction to the acquisition of modern armored warships by several South American countries and was meant to incorporate the latest developments in naval tactics and design. This includes the mounting of her main armament en echelon to allow maximum end-on fire and a heavily-armored citadel amidships to ensure defensive strength. However, due to the state of U.S. industry at the time, Texas's building time was lengthy, and by the time she was commissioned, she was already out of date. Nevertheless, she and the armored cruiser USS Maine were considered advancements in American naval design.
Part of:
Spanish–American War
November 5, 1892 – September 11, 1957
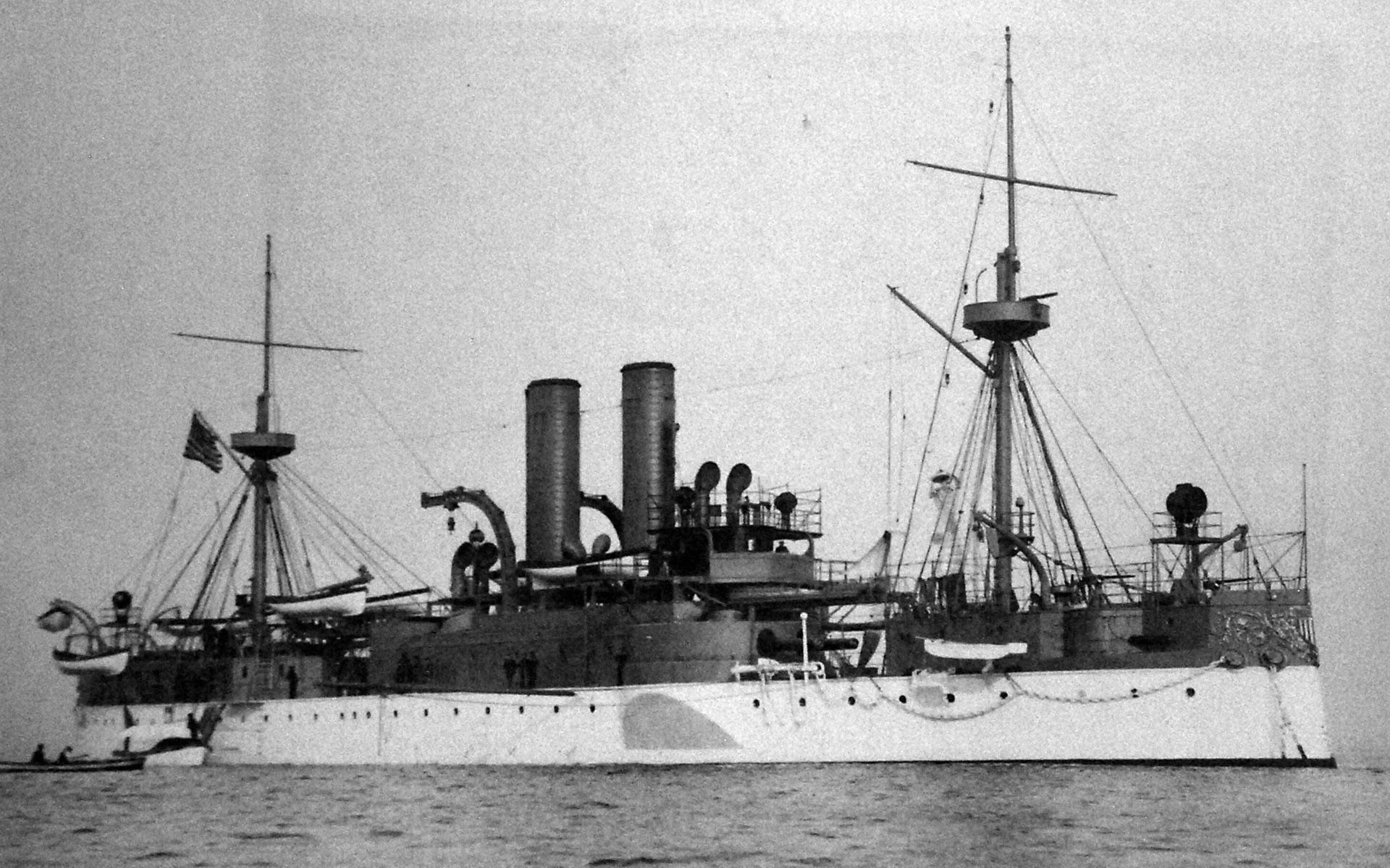
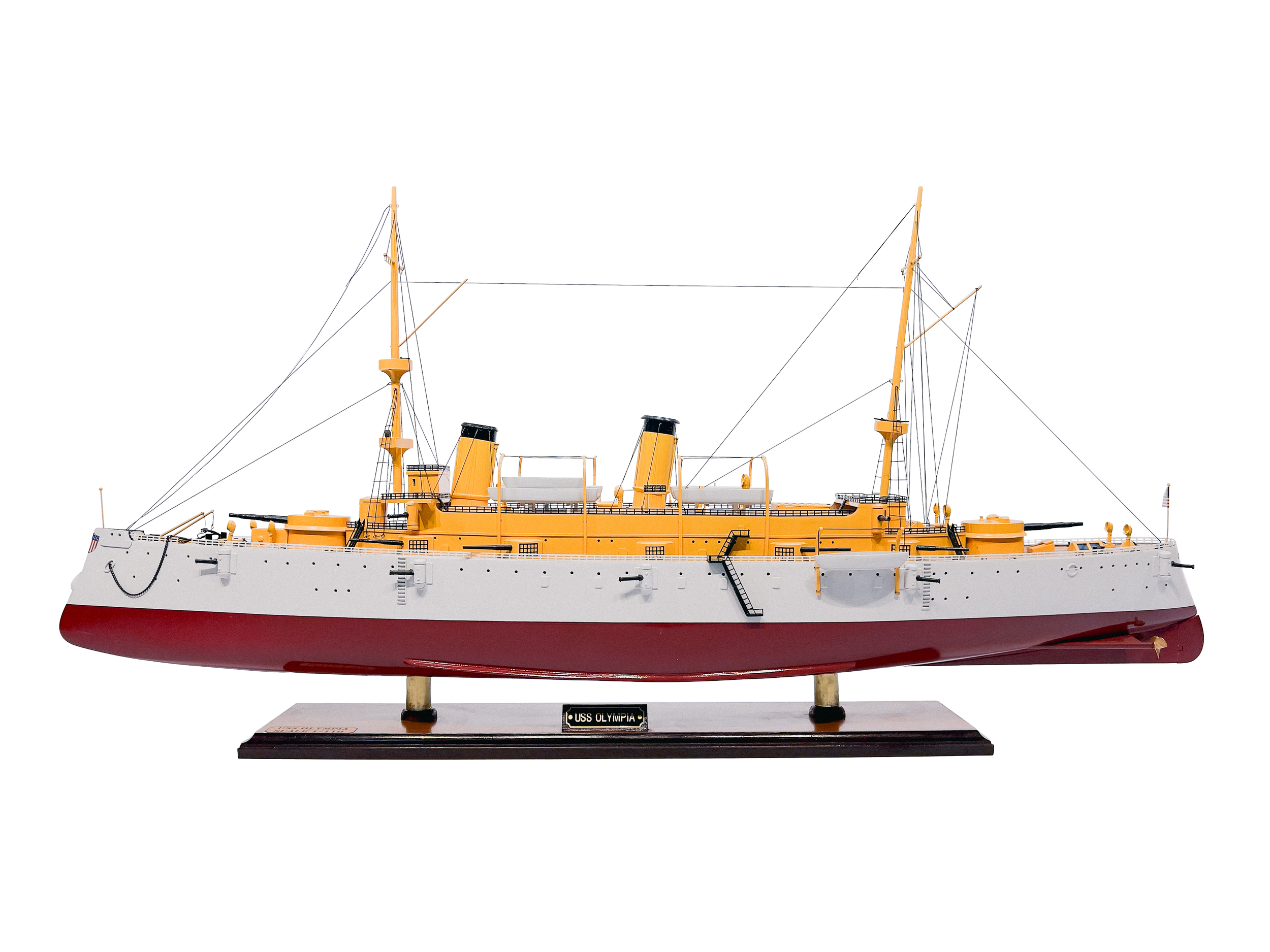
USS Olympia (c–6)
Scale 1/110
The USS Olympia (C-6/CA-15/CL-15/IX-40) is a protected cruiser that saw service with the United States Navy from her commissioning in 1895 until 1922. This vessel became famous as the flagship of Commodore George Dewey during the Battle of Manila Bay in the Spanish–American War in 1898. The ship was decommissioned after returning to the U.S. in 1899 but was returned to active service in 1902.
Part of:
Spanish–American War
World War I
October 26, 1893 – November 2, 1942
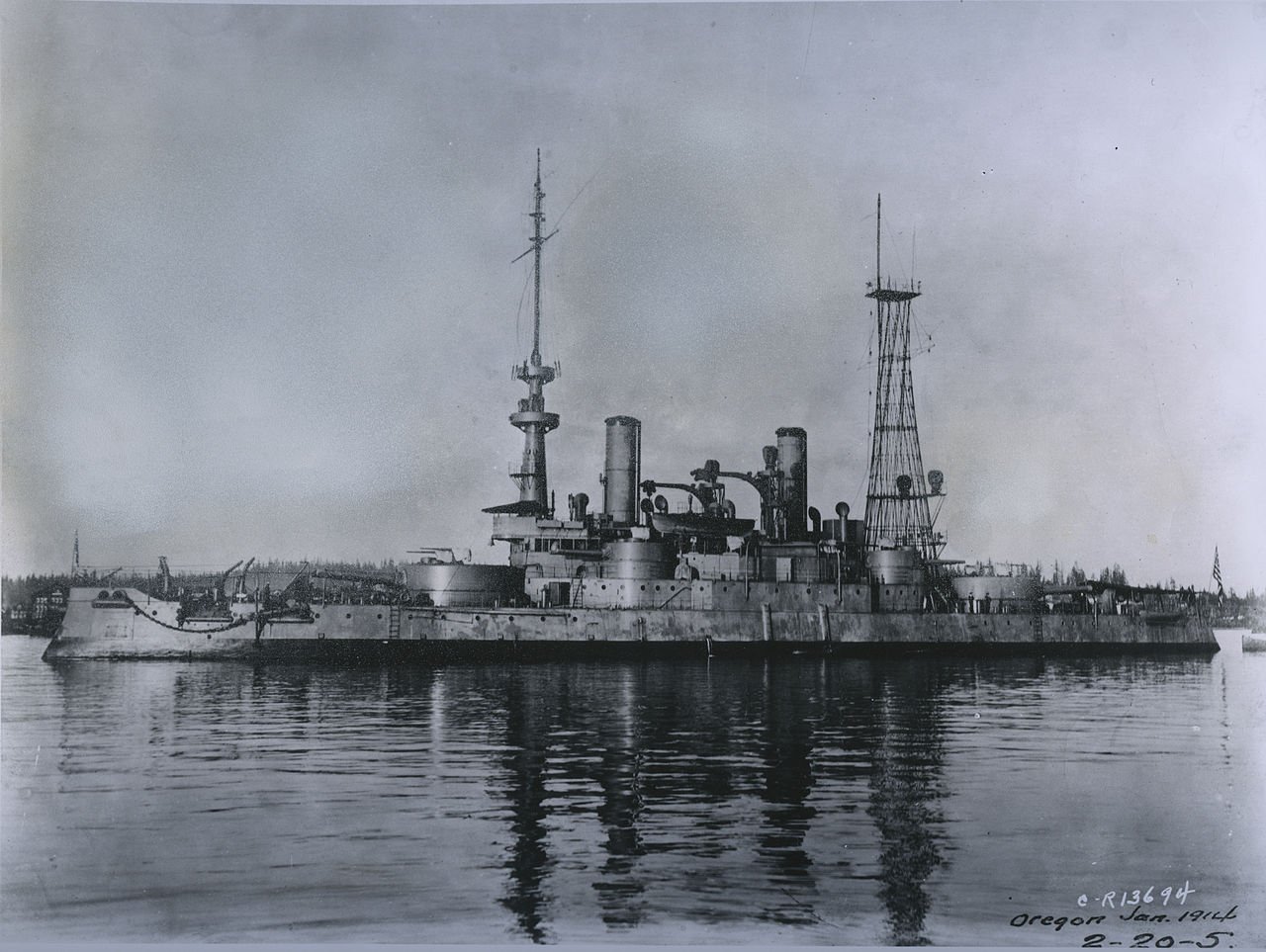
USS Oregon (BB-3)
Scale 1/125
USS Oregon (BB-3) was the third and final member of the Indiana class of pre-dreadnought battleships built for the United States Navy in the 1890s. The three ships were built as part of a modernization program aimed at strengthening the American fleet to prepare for a possible conflict with a European navy. Designed for short-range operations in defense of the United States, the three Indiana-class ships had a low freeboard and carried a main battery of four 13-inch (330 mm) guns in a pair of gun turrets. Oregon and her sister ships were the first modern battleships built for the United States, though they suffered from significant stability and seakeeping problems owing to their small size and insufficient freeboard.
Part of:
Spanish–American War
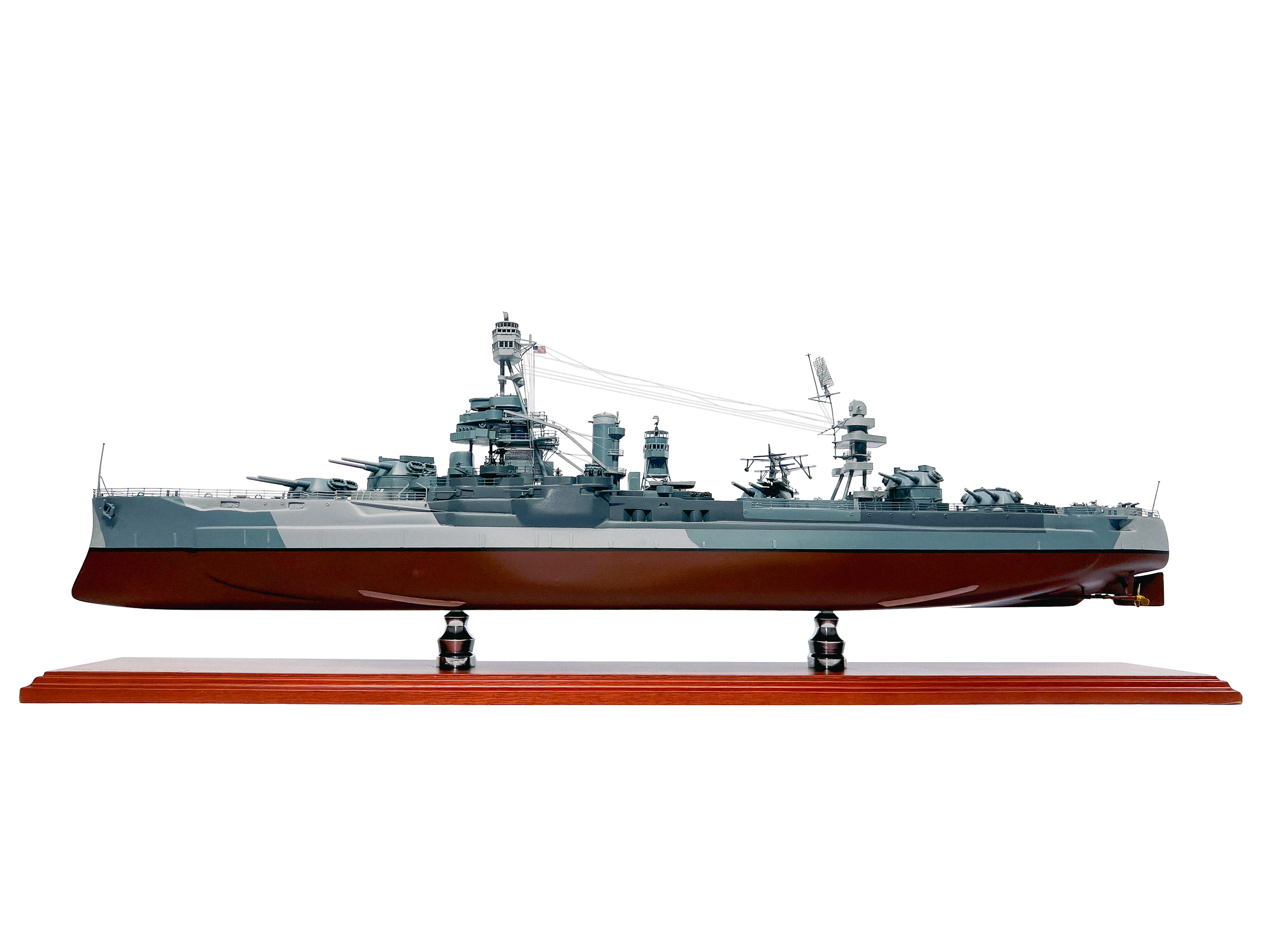
May 18, 1912 – April 30, 1948
USS Texas (BB-35)
Scale 1/192
USS Texas (BB-35) is a museum ship and former United States Navy New York-class battleship. She was launched on 18 May 1912 and commissioned on 12 March 1914.
Part of:
World War I
World War II
D-Day
Battle of Cherbourg

World War I
July 28, 1914 – November 11, 1918
Image: A British officer leads the way "over the top" amid the bursting of German shells. John Warwick Brooke / National Library of Scotland.USS Enterprise (CV-6) was a Yorktown-class carrier built for the United States Navy during the 1930s. She was the seventh U.S. Navy vessel of that name. Colloquially called "The Big E", she was the sixth aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. Launched in 1936, she was one of only three American carriers commissioned before World War II to survive the war (the others being Saratoga and Ranger). She participated in more major actions of the war against Japan than any other United States ship. These actions included the attack on Pearl Harbor — 18 Douglas SBD Dauntless dive bombers of her air group arrived over the harbor during the attack; seven were shot down with eight airmen killed and two wounded, making her the only American aircraft carrier with men at Pearl Harbor during the attack and the first to sustain casualties during the Pacific War— the Battle of Midway, the Battle of the Eastern Solomons, the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands, various other air-sea engagements during the Guadalcanal Campaign, the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and the Battle of Leyte Gulf. Enterprise earned 20 battle stars, the most for any U.S. warship in World War II, and was the most decorated U.S. ship of World War II. She was also the first American ship to sink a full-sized enemy warship after the Pacific War had been declared when her aircraft sank the Japanese submarine I-70 on 10 December 1941.
Part of:
World War II
Pearl Harbor
Doolittle Raid
Battle of Midway
South Pacific
Battle of the Philippine Sea
Battle of Leyte Gulf
October 3, 1936 – 1958
USS Enterprise (CV-6)
Scale 1/48
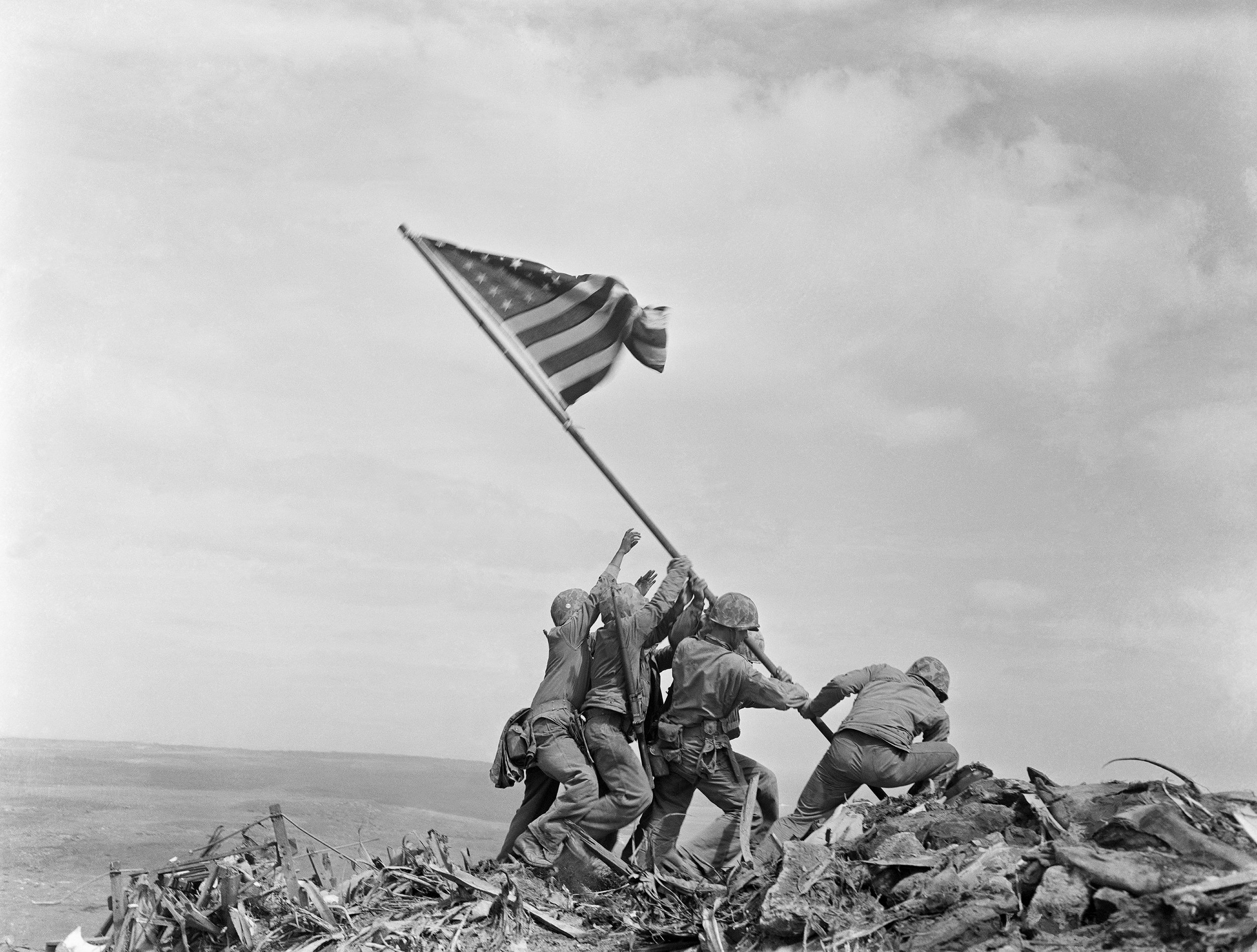

World War II
SEptember 1, 1939 – SEptember 2, 1945
image: THE METROPOLITAN MUSEUM OF ART
February 1942 – July 1945
M4 Sherman
Scale 1/36
The M4 Sherman, officially Medium Tank, M4, was the most widely used medium tank by the United States and Western Allies in World War II. The M4 Sherman proved to be reliable, relatively cheap to produce, and available in great numbers. It was also the basis of several other armored fighting vehicles including self-propelled artillery, tank destroyers, and armored recovery vehicles. Tens of thousands were distributed through the Lend-Lease program to the British Commonwealth and Soviet Union. The tank was named by the British after the American Civil War General William Tecumseh Sherman.
Part of:
World War II
Indonesian National Revolution
Greek Civil War
First Indochina War
1948 Arab–Israeli War
Korean War
Cuban Revolution
Revolución Libertadora
Suez Crisis
1958 Lebanon crisis
Nicaraguan Revolution
Indo-Pakistani War of 1965
Six-Day War
Indo-Pakistani War of 1971
Yom Kippur War
Lebanese Civil War
Uganda–Tanzania War
Iran–Iraq War
June 20, 1942 – August 2, 1943
PT-109
Scale 1/40
PT-109 was an 80-foot Elco PT boat (patrol torpedo boat) last commanded by Lieutenant (junior grade) John F. Kennedy, future United States president, in the Solomon Islands campaign of the Pacific theater during World War II. Kennedy's actions in saving his surviving crew after PT-109 was rammed and sunk by a Japanese destroyer earned him several commendations and made him a war hero. Back problems stemming from the incident required months of hospitalization at Chelsea Naval Hospital and plagued him for the rest of his life. Kennedy's postwar campaigns for elected office referred often to his service on PT-109.
Part of:
World War II
Battle Of Blackett Strait
January 20, 1944 – October 25, 1944
USS Samuel B. Roberts (DE-413)
Scale 1/192
USS Samuel B. Roberts (DE-413) was a John C. Butler-class destroyer escort of the United States Navy that served in World War II, the first of three U.S. Navy ships to bear the name.
Part of:
World War II
Battle Off Samar
January 29, 1944 – January 12, 1995
USS Missouri
Scale 1/200
USS Missouri (BB-63) is an Iowa-class battleship built for the United States Navy (USN) in the 1940s and is currently a museum ship. Completed in 1944, she is the last battleship commissioned by the United States. The ship was assigned to the Pacific Theater during World War II, where she participated in the Battles of Iwo Jima and Okinawa and shelled the Japanese home islands. Her quarterdeck was the site of the surrender of the Empire of Japan, which ended World War II.
Part of:
World War II
Korean War
Gulf War
March 12, 1947 - December 26, 1991
Cold War
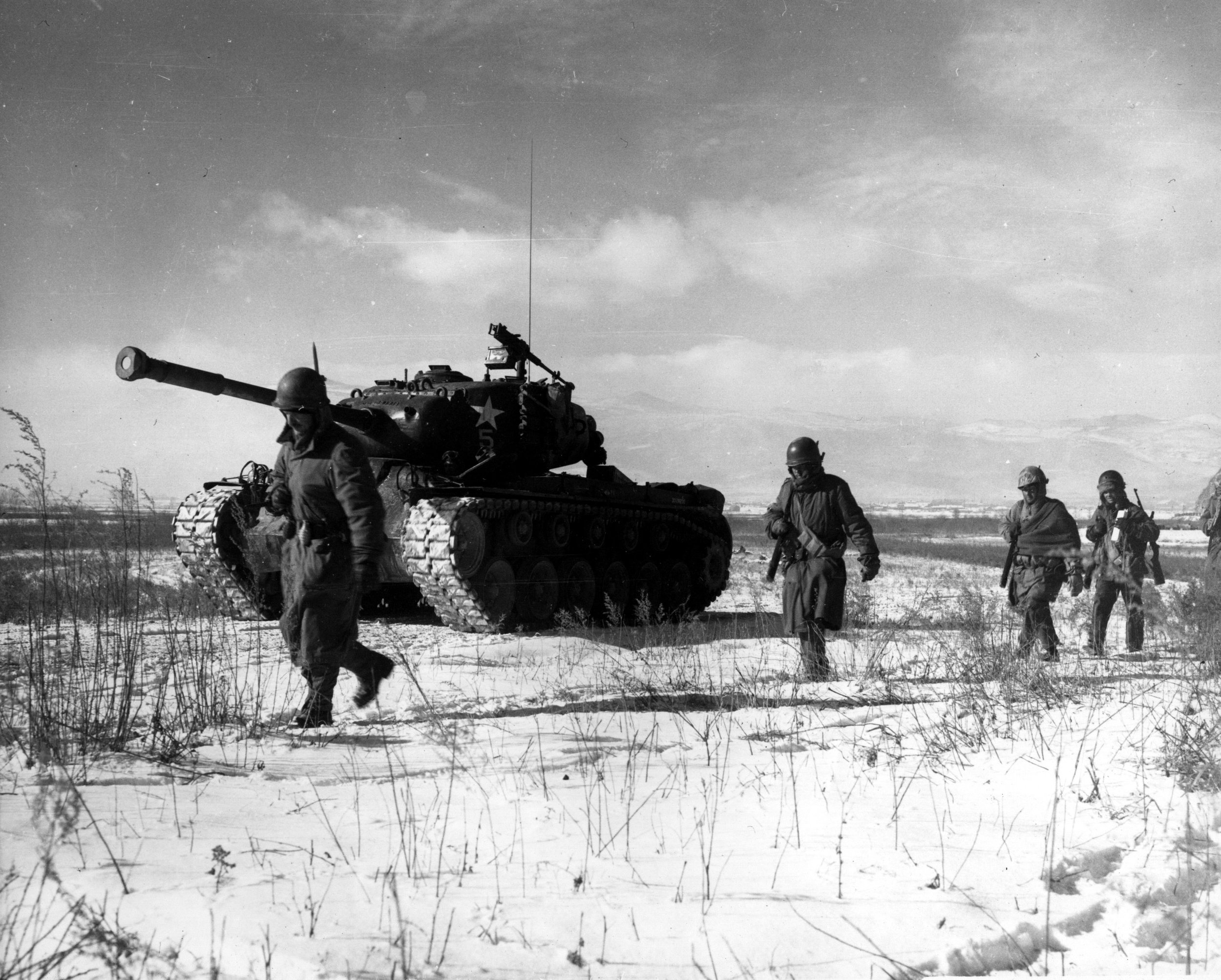

Korean War
June 25, 1950 – July 27, 1953
Image: A column of troops and armor of the 1st Marine Division move through communist Chinese lines during their successful breakout from the Chosin Reservoir in North Korea. Photo by Corporal Peter McDonald/U.S. Marine Corps.The M48 Patton is an American first-generation main battle tank (MBT) introduced in February 1952, being designated as the 90mm Gun Tank: M48. It was designed as a replacement for the M26 Pershing, M4 Sherman, M46, and M47 Patton tanks, and was the main battle tank of the U.S. Army and U.S. Marine Corps in the Vietnam War (and the first American MBT). Nearly 12,000 M48s were built, mainly by Chrysler and American Locomotive Company, from 1952 to 1961. The M48 Patton was the first U.S. medium gun tank with a four-man crew, featuring a centerline driver's compartment and no bow machine gunner. As with nearly all new armored vehicles, it had a wide variety of suspension systems, cupola styles, power packs, fenders, and other details among individual tanks.
Part of:
Cold War
1958 Lebanon crisis
Portuguese Colonial War
Dominican Civil War
Vietnam War
Six-Day War
Indo-Pakistani War of 1965
Indo-Pakistani War of 1971
Yom Kippur War
Western Sahara War
Lebanese Civil War
Turkish invasion of Cyprus
Iran–Iraq War
Battle of Mogadishu (1993)
Kurdish–Turkish conflict
2007 Lebanon conflict
1952 – Present
M48 Patton
Scale 1/36
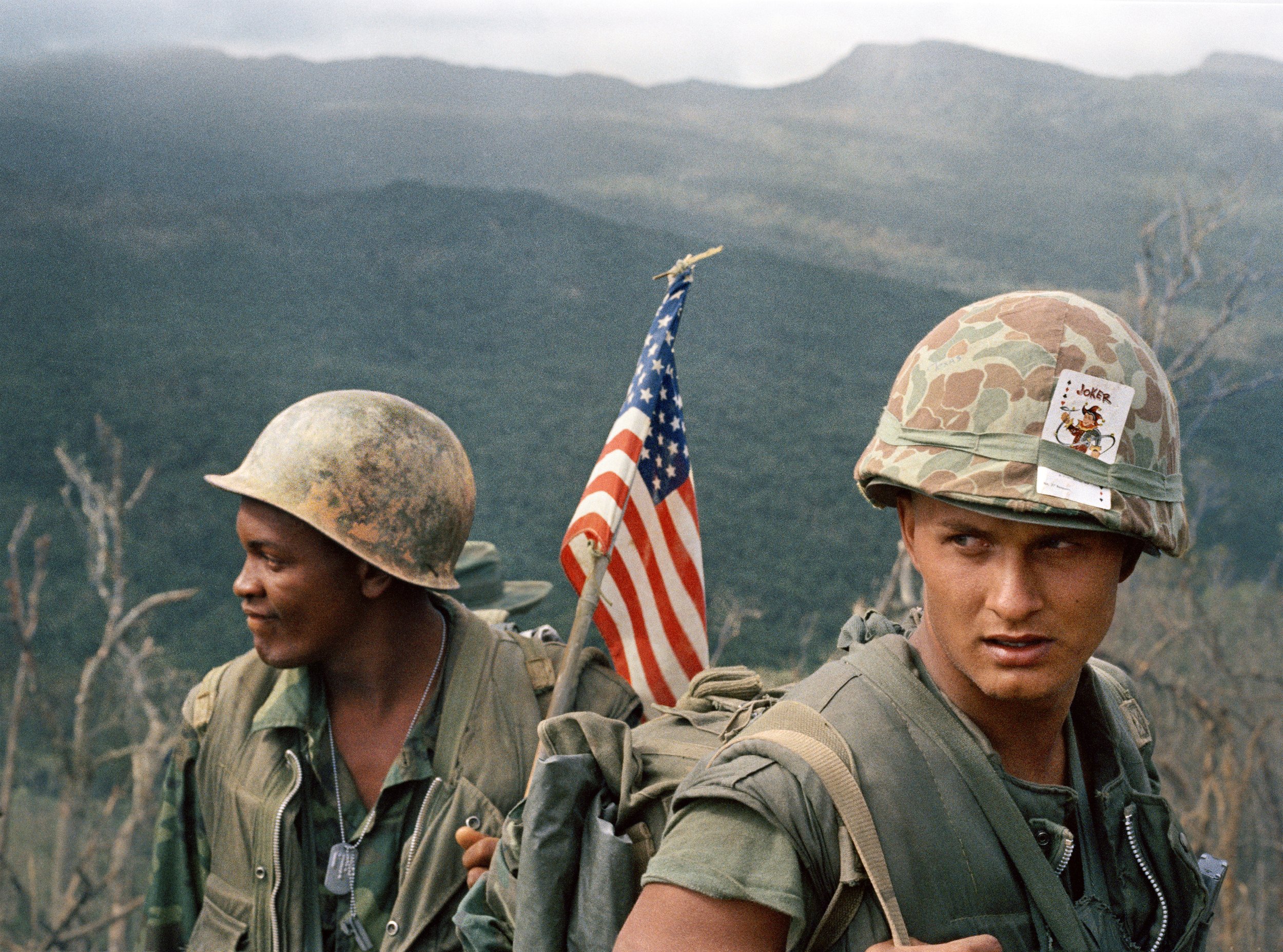

Vietnam War
November 1, 1955 – April 30, 1975
Image: U.S. Marines moving through a landing zone in Vietnam, taken in December 1969, is part of the exhibit at the Huntsville Museum of Art. Patrol Boat, Riverine, or PBR, is the United States Navy designation for a small rigid-hulled patrol boat used in the Vietnam War from March 1966 until 1975. They were deployed in a force that grew to 250 boats, the most common craft in the River Patrol Force, Task Force 116, and were used to stop and search river traffic in areas such as the Mekong Delta, the Rung Sat Special Zone, the Saigon River and in I Corps, in the area assigned to Task Force Clearwater, in an attempt to disrupt weapons shipments. In this role, they frequently became involved in firefights with enemy soldiers on boats and on the shore, were used to insert and extract Navy SEAL teams, and were employed by the United States Army's 458th Transportation Company, known as the 458th Sea Tigers.
Part of:
Vietnam War
1966 – 1975